12.6 Backcasting
Sometimes it is useful to “backcast” a time series — that is, forecast in reverse time. Although there are no in-built R functions to do this, it is very easy to implement. The following functions reverse a ts object and a forecast object.
# Function to reverse time
reverse_ts <- function(y)
{
ts(rev(y), start=tsp(y)[1L], frequency=frequency(y))
}
# Function to reverse a forecast
reverse_forecast <- function(object)
{
h <- length(object$mean)
f <- frequency(object$mean)
object$x <- reverse_ts(object$x)
object$mean <- ts(rev(object$mean),
end=tsp(object$x)[1L]-1/f, frequency=f)
object$lower <- object$lower[h:1L,]
object$upper <- object$upper[h:1L,]
return(object)
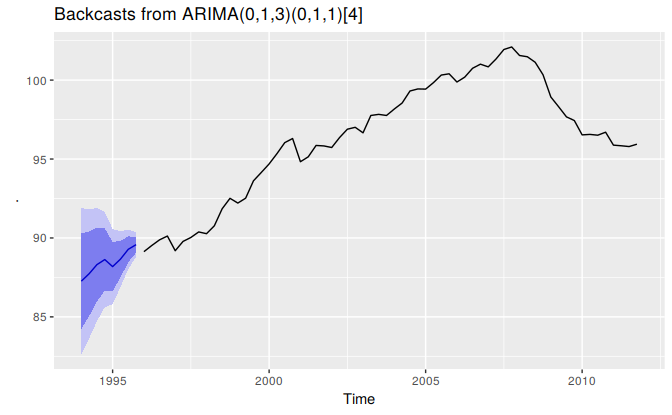
}Then we can apply these function to backcast any time series. Here is an example applied to quarterly retail trade in the Euro area. The data are from 1996-2011. We backcast to predict the years 1994-1995.
# Backcast example
euretail %>%
reverse_ts() %>%
auto.arima() %>%
forecast() %>%
reverse_forecast() -> bc
autoplot(bc) + ggtitle(paste("Backcasts from",bc$method))