setTolerance
Set the tolerance for the solver
Set the tolerance for the solver
setTolerance(object, tol) setTolerance(object, ...) <- value
Arguments
| object | a class object |
|---|---|
| tol | tolerance |
| ... | additional parameters |
| value | a value to set |
Details
Sets the tolerance like this: odeSolver <- setTolerance(odeSolver, tol)
Sets the tolerance like this: setTolerance(odeSolver) <- tol
Examples
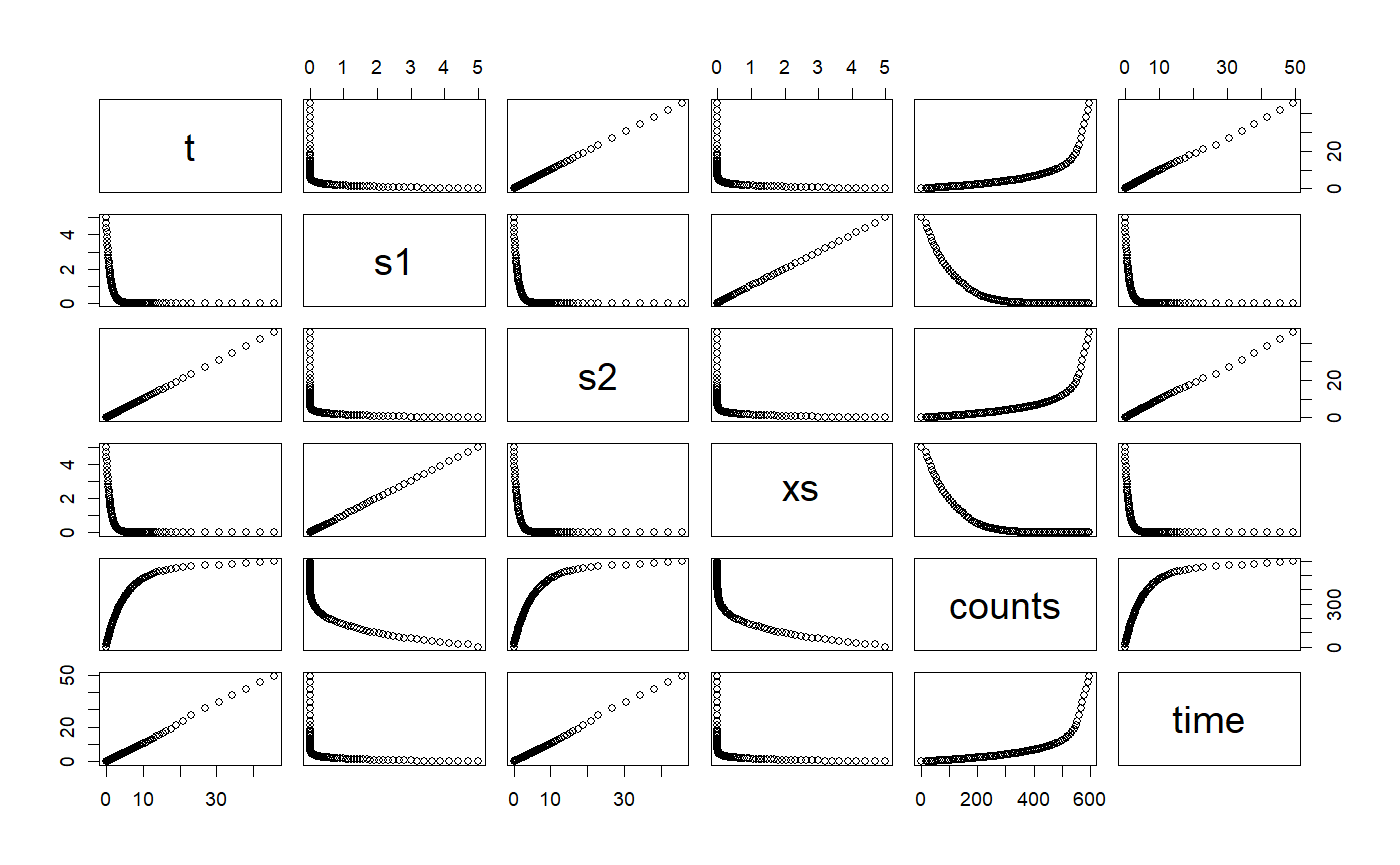
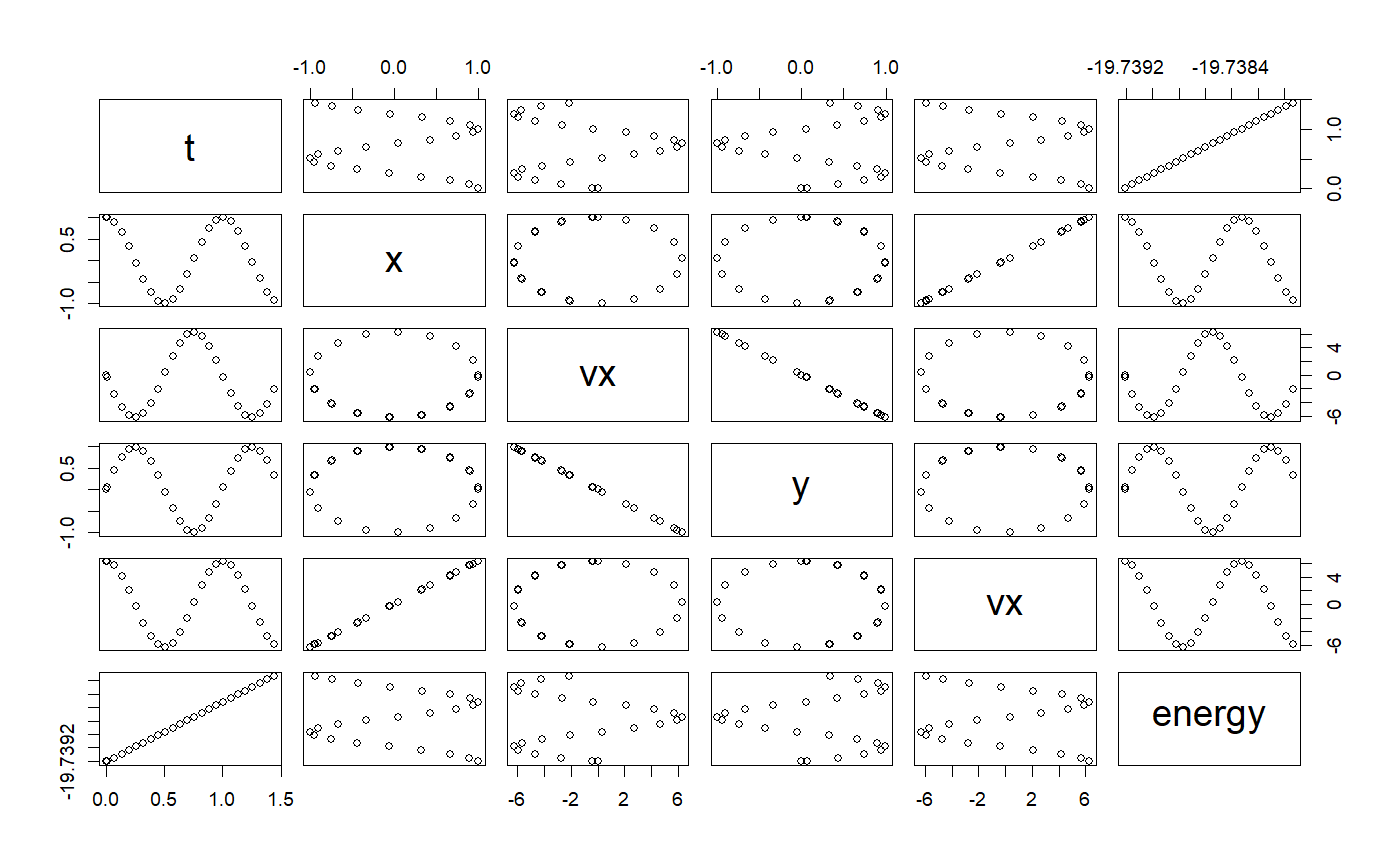
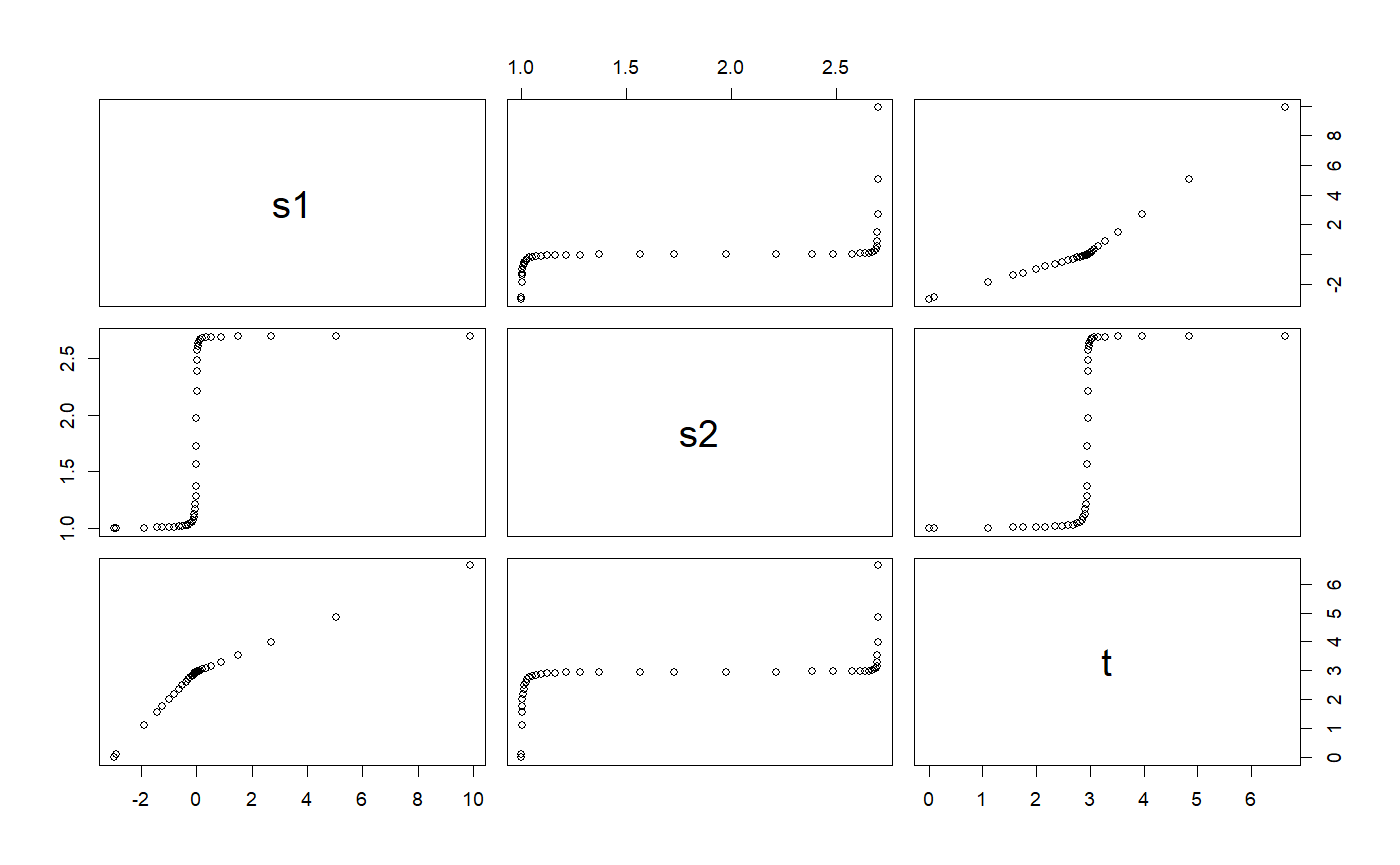
# ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ example: ComparisonRK45App.R # Compares the solution by the RK45 ODE solver versus the analytical solution # Example file: ComparisonRK45App.R # ODE Solver: Runge-Kutta 45 # ODE class : RK45 # Base class: ODETest importFromExamples("ODETest.R") ComparisonRK45App <- function(verbose = FALSE) { ode <- new("ODETest") # create an `ODETest` object ode_solver <- RK45(ode) # select the ODE solver ode_solver <- setStepSize(ode_solver, 1) # set the step # Two ways of setting the tolerance # ode_solver <- setTolerance(ode_solver, 1e-8) # set the tolerance setTolerance(ode_solver) <- 1e-8 time <- 0 rowVector <- vector("list") i <- 1 while (time < 50) { rowVector[[i]] <- list(t = getState(ode)[2], s1 = getState(ode)[1], s2 = getState(ode)[2], xs = getExactSolution(ode, time), counts = getRateCounts(ode), time = time ) ode_solver <- step(ode_solver) # advance one step stepSize <- getStepSize(ode_solver) time <- time + stepSize ode <- getODE(ode_solver) # get updated ODE object i <- i + 1 } return(data.table::rbindlist(rowVector)) # a data table with the results } # show solution solution <- ComparisonRK45App() # run the example plot(solution)# ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ example: KeplerDormandPrince45App.R # Demostration of the use of ODE solver RK45 for a particle subjected to # a inverse-law force. The difference with the example KeplerApp is we are # seeing the effect in thex and y axis on the particle. # The original routine used the Verlet ODE solver importFromExamples("KeplerDormandPrince45.R") set_solver <- function(ode_object, solver) { slot(ode_object, "odeSolver") <- solver ode_object } KeplerDormandPrince45App <- function(verbose = FALSE) { # values for the examples x <- 1 vx <- 0 y <- 0 vy <- 2 * pi dt <- 0.01 # step size tol <- 1e-3 # tolerance particle <- KeplerDormandPrince45() # use class Kepler # Two ways of initializing the ODE object # particle <- init(particle, c(x, vx, y, vy, 0)) # enter state vector init(particle) <- c(x, vx, y, vy, 0) odeSolver <- DormandPrince45(particle) # select the ODE solver # Two ways of initializing the solver # odeSolver <- init(odeSolver, dt) # start the solver init(odeSolver) <- dt # Two ways of setting the tolerance # odeSolver <- setTolerance(odeSolver, tol) # this works for adaptive solvers setTolerance(odeSolver) <- tol setSolver(particle) <- odeSolver initialEnergy <- getEnergy(particle) # calculate the energy rowVector <- vector("list") i <- 1 while (getTime(particle) < 1.5) { rowVector[[i]] <- list(t = getState(particle)[5], x = getState(particle)[1], vx = getState(particle)[2], y = getState(particle)[3], vx = getState(particle)[4], energy = getEnergy(particle) ) particle <- doStep(particle) # advance one step energy <- getEnergy(particle) # calculate energy i <- i + 1 } DT <- data.table::rbindlist(rowVector) return(DT) } solution <- KeplerDormandPrince45App() plot(solution)importFromExamples("AdaptiveStep.R") # running function AdaptiveStepApp <- function(verbose = FALSE) { ode <- new("Impulse") ode_solver <- RK45(ode) # Two ways to initialize the solver # ode_solver <- init(ode_solver, 0.1) init(ode_solver) <- 0.1 # two ways to set tolerance # ode_solver <- setTolerance(ode_solver, 1.0e-4) setTolerance(ode_solver) <- 1.0e-4 i <- 1; rowVector <- vector("list") while (getState(ode)[1] < 12) { rowVector[[i]] <- list(s1 = getState(ode)[1], s2 = getState(ode)[2], t = getState(ode)[3]) ode_solver <- step(ode_solver) ode <- getODE(ode_solver) i <- i + 1 } return(data.table::rbindlist(rowVector)) } # run application solution <- AdaptiveStepApp() plot(solution)