RK4 class
RK4 class
RK4 generic
RK4 class constructor
RK4(ode, ...) # S4 method for RK4 init(object, stepSize, ...) # S4 method for RK4 init(object, ...) <- value # S4 method for RK4 step(object, ...) # S4 method for ODE RK4(ode, ...)
Arguments
| ode | an ODE object |
|---|---|
| ... | additional parameters |
| object | internal passing object |
| stepSize | the size of the step |
| value | value for the step |
Examples
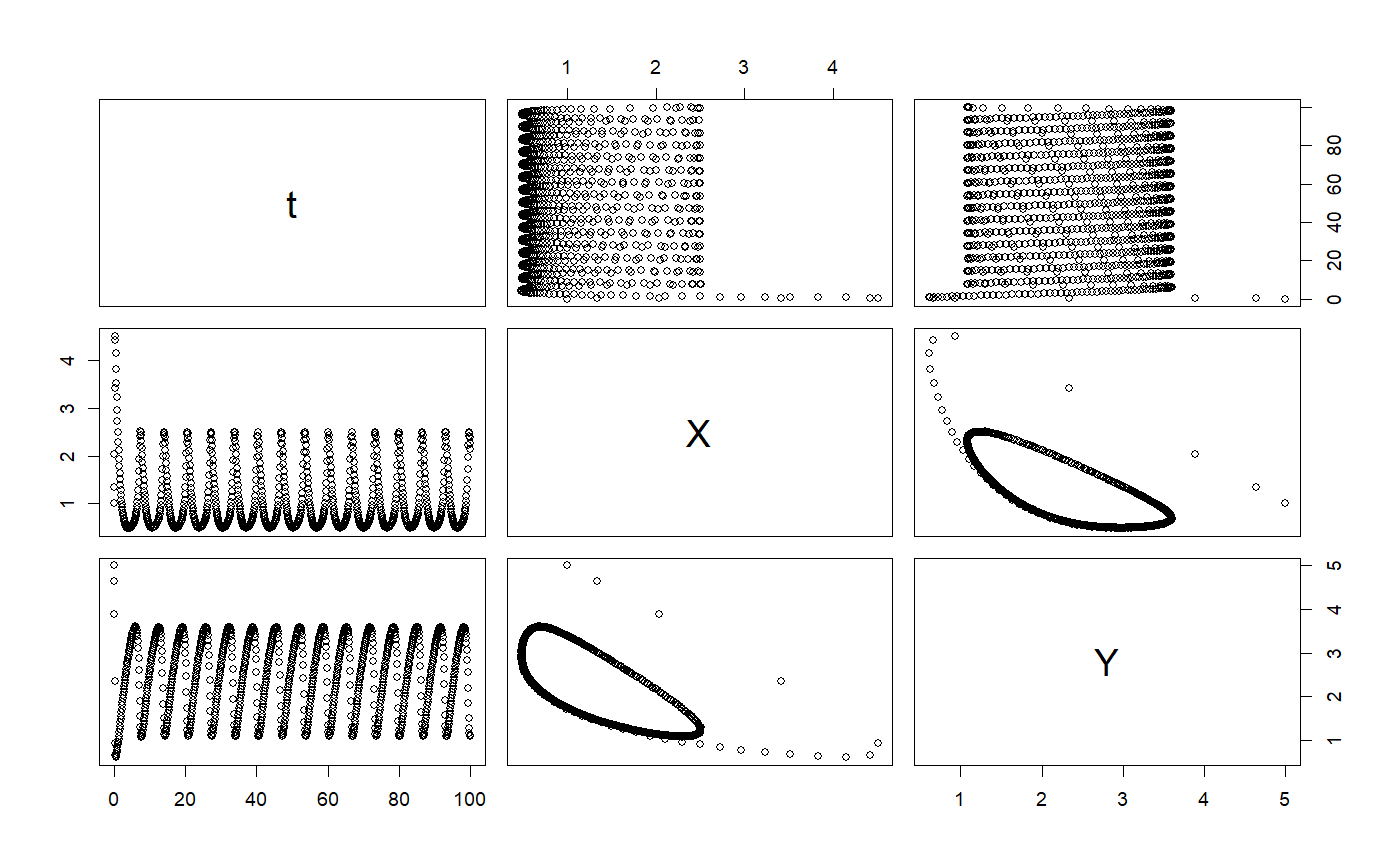
# ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ base class: Projectile.R # Projectile class to be solved with Euler method setClass("Projectile", slots = c( g = "numeric", odeSolver = "RK4" ), prototype = prototype( g = 9.8 ), contains = c("ODE") ) setMethod("initialize", "Projectile", function(.Object) { .Object@odeSolver <- RK4(.Object) return(.Object) })#> [1] "initialize"setMethod("setStepSize", "Projectile", function(object, stepSize, ...) { # use explicit parameter declaration # setStepSize generic has two step parameters: stepSize and dt object@odeSolver <- setStepSize(object@odeSolver, stepSize) object })#> [1] "setStepSize"setMethod("step", "Projectile", function(object) { object@odeSolver <- step(object@odeSolver) object@rate <- object@odeSolver@ode@rate object@state <- object@odeSolver@ode@state object })#> [1] "step"setMethod("setState", signature("Projectile"), function(object, x, vx, y, vy, ...) { object@state[1] <- x object@state[2] <- vx object@state[3] <- y object@state[4] <- vy object@state[5] <- 0 # t + dt object@odeSolver@ode@state <- object@state object })#> [1] "setState"setMethod("getState", "Projectile", function(object) { object@state })#> [1] "getState"setMethod("getRate", "Projectile", function(object, state, ...) { object@rate[1] <- state[2] # rate of change of x object@rate[2] <- 0 # rate of change of vx object@rate[3] <- state[4] # rate of change of y object@rate[4] <- - object@g # rate of change of vy object@rate[5] <- 1 # dt/dt = 1 object@rate })#> [1] "getRate"# constructor Projectile <- function() new("Projectile") # ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ example: PendulumApp.R # Simulation of a pendulum using the EulerRichardson ODE solver suppressPackageStartupMessages(library(ggplot2)) importFromExamples("Pendulum.R") # source the class PendulumApp <- function(verbose = FALSE) { # initial values theta <- 0.2 thetaDot <- 0 dt <- 0.1 pendulum <- Pendulum() # pendulum@state[3] <- 0 # set time to zero, t = 0 pendulum <- setState(pendulum, theta, thetaDot) pendulum <- setStepSize(pendulum, dt = dt) # using stepSize in RK4 pendulum@odeSolver <- setStepSize(pendulum@odeSolver, dt) # set new step size rowvec <- vector("list") i <- 1 while (getState(pendulum)[3] <= 40) { rowvec[[i]] <- list(t = getState(pendulum)[3], # time theta = getState(pendulum)[1], # angle thetadot = getState(pendulum)[2]) # derivative of angle pendulum <- step(pendulum) i <- i + 1 } DT <- data.table::rbindlist(rowvec) return(DT) } # show solution solution <- PendulumApp() plot(solution)# +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ application: ReactionApp.R # ReactionApp solves an autocatalytic oscillating chemical # reaction (Brusselator model) using # a fourth-order Runge-Kutta algorithm. importFromExamples("Reaction.R") # source the class ReactionApp <- function(verbose = FALSE) { X <- 1; Y <- 5; dt <- 0.1 reaction <- Reaction(c(X, Y, 0)) solver <- RK4(reaction) rowvec <- vector("list") i <- 1 while (getState(reaction)[3] < 100) { # stop at t = 100 rowvec[[i]] <- list(t = getState(reaction)[3], X = getState(reaction)[1], Y = getState(reaction)[2]) solver <- step(solver) reaction <- getODE(solver) i <- i + 1 } DT <- data.table::rbindlist(rowvec) return(DT) } solution <- ReactionApp()#>#>plot(solution)